Case Study: How to Ensure Safety While Manufacturing Highly Potent APIs
Highly potent active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) require careful attention to safety and handling during formulation and manufacturing. This blog explores the process required for manufacturing a highly potent API for an ophthalmic indication, based on a case study involving loteprednol etabonate, a topical corticosteroid used to treat eye inflammations.
What are Highly Potent APIs?
Highly potent APIs elicit strong biological activity at minimal concentrations. They are defined as substances that are biologically active at approximately 150µm/kg in humans. Their high potency brings therapeutic advantages, but also introduces risks during manufacturing due to potential exposure.
They are often used in the treatment of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and lupus, as well as central nervous system (CNS) disorders like Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and epilepsy.
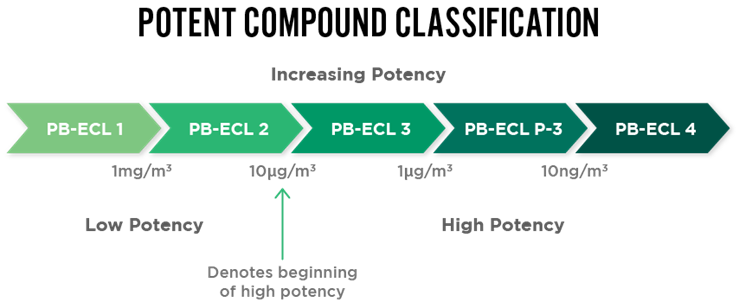
New APIs undergo robust evaluation to determine their classification level for safe handling procedures and clearance limits. Performance-based exposure control limit (PB-ECL) is used to correctly classify the compound (Class 1 to Class 4).
REGUATORY REQUIREMENTS IN MANUFACTURING HIGHLY POTENT HPAPIS
Regulatory agencies all over the world have stringent requirements when it comes to the safe and appropriate manufacture of HPAPI products. Due to the high potency of HPAPIs, these regulatory agencies emphasize rigorous containment measures such as separation of operations and cleaning validation, to ensure worker safety and prevent cross-contamination between products.
Regardless of the agency, recommendations from the FDA’s Q7 Good Manufacturing Practice Guidance for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Health Canada’s GUI-0104 guideline, or Australia’s Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA)’s GMP Clearance for Overseas Manufacturers guidelines, all focus on a handful of key considerations in ensuring safe HPAPI manufacturing: containment and cross-contamination prevention, occupational safety, and quality assurance.
Nanomilling enhances the dissolution rate of poorly soluble APIs, improving their absorption and potentially increasing therapeutic efficacy.
They also stress the importance of stringent verification and documentation to ensure that all cleaning procedures are effective at removing residues of HPAPIs, cleaning agents, and other contaminants from equipment and surfaces. Segregated facilities and equipment for product manufacture according to their compounds are typically required.
The Challenge: Safe Manufacture of Highly Potent APIs
Exposure to highly potent APIs must be carefully managed during production. This calls for specialized facilities, protective measures, and expert handling for the safety of both workers and the environment.
A long-term client tasked Altasciences with manufacturing a nanomilled suspension of a loteprednol etabonate intermediate for an ophthalmic application. Loteprednol etabonate, a corticosteroid, requires stringent safety protocols due to its classification as a highly potent API. We developed the drug from R&D to commercialization, maintaining our high standard of safe handling and processing procedures throughout the project.

Key Steps in the Process
1. Safety Protocols and Hazard Control:
To manage the inherent risks of HPAPIs, we followed industrial hygiene protocols. We anticipated potential hazards and recognized and evaluated all potential exposure events to mitigate risk. Identifying exposure events early on—particularly for the dispensing of the API into the vehicle—enabled our experts to implement appropriate containment measures.
In compliance with regulatory requirements, our team operated within state-of-the-art high-potency Grade C and D areas, with robust registrations and licenses that include FDA drug establishment registration, DEA licensing (Schedules I-V and List I), and FDA food facility registration.
2. API Identification:
Compound potency is classified via the occupational exposure limit (OEL) or operational exposure band (OEB) when little information is available. The classifications range from 1 to 4, with lower classification values indicating more potent compounds, which require greater levels of containment and safety precautions at the manufacturing site.
Based on available toxicological data, we were able to identify loteprednol etabonate as an OEB 3 compound. Known to be a reproductive toxin and harmful to aquatic life, it required careful containment measures during production.
3. Engineering and Administrative Controls:
Safe highly potent API manufacturing lies in strict controls and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE). Our staff wore double nitrile gloves, full-body protective suits, respirators, and safety goggles. Engineering controls, such as airlocks and pressure-controlled rooms with Magnehelic gauges for monitoring, further minimized the risk of airborne contamination and cross-contamination.

Technicians must limit exposure to the ingredient to prevent short- and long-term health risks, necessitating specialized facilities, equipment, and personnel.
Production took place in a Grade C cleanroom—a completely isolated unit that keeps airborne particulates down. These isolated suites feature containment systems for negative pressure controls to limit exposure, and for monitoring and verifying effectiveness of the containment strategies. With airlocks around the manufacturing and laboratory areas, staff could safely gown and de-gown. Furthermore, laminar flow systems were utilized with HEPA filters for superior air filtration, reducing the risk of disrupting airborne particles. When handling loteprednol etabonate, additional containment strategies were applied to reduce aerosolization.
4. Product Disposal:
We disposed of all waste and material generated from the manufacturing loteprednol etabonate at regulated chemical treatment facilities. Proper documentation and disposal protocols ensured compliance with environmental and safety standards.
Altasciences’ Commitment to Excellence
We have decades of experience handling highly potent APIs, from formulation to manufacturing. We can manage highly potent API projects from start to finish within our own facility, with analytical, manufacturing, and cGMP warehouse capacity. With segregated Grade C and D cleanrooms, specialized training for operators, and state-of-the-art containment systems, even the most potent compounds can be handled safely. At the beginning of each highly potent API program, operators receive refresher training on the specifics of engineering controls and safety measures required for handling the API in question.
Are you working on a highly potent API? Contact us today to get your program on track.
This blog was originally published in November, 2024, and updated in January 2025.



